UX in search engines is a quite unconventional approach to optimizing search results, known more widely as Positioning or SEO (Search engine optimization). Before Google published the report about the 4 key moments in making decisions and shaping user preferences, the positioning process had focused mainly on ranking factors, which were beneficial only from the point of view of crawling and indexing bots. That resulted in an increase of the visibility of websites in organic results.
If there were two websites that had the same technological solutions, a full optimization process was carried out on both. The one that obtained more links from better quality websites was usually the winner. Thus, the natural direction of SEO development for many years was to direct traffic to the website, regardless of whether the website was able to serve the user and bring him/her to conversion effectively.
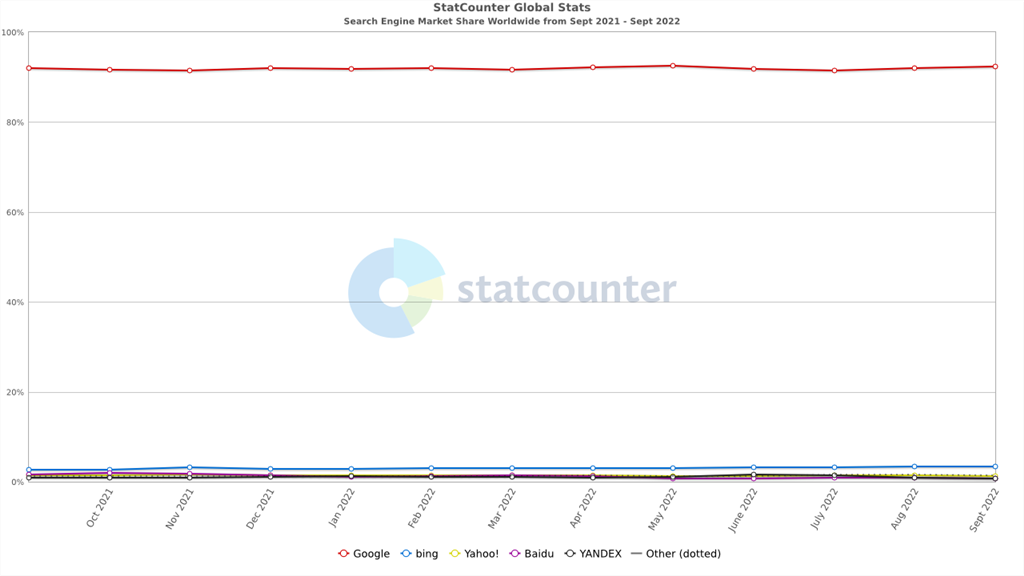
Taking into the consideration the point of view of the creators of the search engine, it can be assumed that the lack of useful results does more harm than good. Users usually receive a list of artificially selected SERPs instead of getting results that are supposed to meet their needs. That does not build trust among the enthusiasts of online keyword searches. As a consequence, the lack of fulfilling users’ needs increases the search engine market share and it opens the door more and more widely to other entities, such as:
- Bing (3.34%),
- Yahoo (1.34%),
- Yandex (0.96%),
- Baidu (0.83%),
- DuckDuckGo (0.71%).
Evolution of search results in terms of User Experience
Over the years, Google’s search engine struggled with the creativity of webmasters and more technical SEOs by giving them into consideration official and unofficial actions in order to update search results. Above all, the search results were always supposed to be:
- relevant
- expert
- fast
The dream of Google was to create for its users a place where they would come for knowledge, services, products, etc. Google still has been dreaming about it.
Looking through the prism of last years, it is very easy to distinguish 3 main trends of changes in search algorithms. From the point of view of a search engine, as well as of the user, the algorithms aim at increasing the usefulness of search results and that affects the length of time spent by users, nota bene, in the search engine!
Optimizing search results based on Match

Google Koliber Algorithm
In 2013 Google came up with the attempt to deal with cluttered search results. The update called Koliber was intended to put pressure on content creators to make them respond better to the needs of users while creating the content (not only in text form). Koliber was just the beginning of changes thanks to the introduction of the mechanisms of guessing the context of the content on websites.
Google Rankbrain Algorithm
We did not wait long for the next episode of the SERP’s relevance series. In 2015 Google announced the implementation of a new algorithm called Rankbrain. It was supposed to keep an eye on the content on specific subpages of websites to guarantee that the content reflected the intentions of users’ queries in the search engine. From that moment, it became even more important to optimize the content for contextual search.
Google BERT Algorithm
The announcement of BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) algorithm turned out to cross the “T’s, dot the”I’s in 2019. The algorithm dealt with natural language processing using neural networks. It enabled Google to make search results even more dependent on matching them to the intention of the query in the context of the entire content, and not particularly selected keywords.
Google MUM Update
The update of search results which is based on matching the content to the intentions of users in the recent version is called MUM (Multitask Unified Model). It was released in mid-2021. Although this update works similarly to Bert, it understands not only content in the form of text, but also in the form of image, video and sound. Since technology and innovation never stand still for too long, that is probably not the last word from Google engineers. Especially for the new generation of search engine users, the so-called native searchers for whom the contextual search by image, video and sound is a natural cognitive process.
Optimizing search results based on Authority

Google Panda Algorithm
To understand the concept of this trend, let us go back for a moment to the year 2011, in which Google came up with the idea of introducing periodic updates called Panda. The updates were described as the busters of spam and low-quality content which were not intended to help the end user, but to collect traffic and monetize it effectively. (Panda has been a part of the main search result update algorithm since 2016)
Google E-A-T Algorithm
Before Google introduced content ranking signals to the main thread in 2014, a new update with the mysterious name E-A-T was announced. It is an abbreviation of Expertise, Authority and Trust. Its name suggests that those websites which relied heavily on expert content and the author’s authority can benefit from being treated as favourite of the search. Such websites were supposed to strengthen the trust in the content consumer and inspire positive experiences.
Google Medic Update
As it happens with Google, each update has its own wider context. In 2018 Google launched another algorithm update called Medic, in which the E-A-T concept became a part of a wider YMYL (Your Money Your Life) thread. Medic mainly affected Health, Finance and Wellness industries, in which the content, by definition, should be pro-consumer, expert and reliable, not typically sales-focused.
Helpful Content Update
It is the recent installment of the ranking algorithm update (08-2022). Its purpose is to reward content that guarantees satisfaction and brings value from the perspective of the user, not of the search engine. This is not a Core Update, but rather a new set of variables thrown into the modes of the Machine Learning algorithm. The impact of updating the ranking is perceived primarily on websites that generate large amounts of low-value content, have little added value or are simply of little use.
Optimizing search results based on Speed

Google Mobile-Friendly Update
Speed is crucial for online consumers. Not only do they want to shop quickly, they also desire to reach fast the end of their cognitive journey which starts in the search results on their smartphones. Therefore, Google came up with the idea to announce 2016 as the year of Mobilegedon. Then, users of mobile search results could count on the support of the search engine in terms of: adapting websites to mobile devices, safe browsing, SSL secured websites, reducing full-screen ads and pop-ups covering the main content.
Google Mobile Speed Update
The next step was the materialization of the mobility trend in search results. Although it was announced in 2018 as Mobile First Indexing Update, it did not enter into force until the beginning of 2021. Google announced also in 2018 that the speed on mobile devices would becoming one of the factors ranking. We were waiting for this change from the moment in which the Desktop Speed officially entered as a ranking factor for all results in 2010.
Google Page Experience Algorithm
At the end of the “speed trend”, there was an update nicely called Page Experience Update.
It included:
- Page Performance, i.e. the speed of the website interaction,
- User Experience, i.e. the usefulness of the website
- Mobile, i.e. the availability of the website on mobile devices
The entire concept of Page Experience was completed with user-oriented performance metrics called Core Web Vitals in 2020. Page Experience Signals were included in the ranking factors of the main search engine algorithm in 2021. It is interesting that Page Performance is also applied to desktop search results. However, the date of the extension for the desktop results still remains unconfirmed.
Search Experience Optimization at the service of the user
Aa far as the recent official and unofficial changes to organic search results are concerned, a catchy trend has emerged: Search Experience Optimization.
SXO is the optimization of user experience at the following levels:
- search results (SERP Experience),
- websites (Site Experience):
- code correctness (Web Dev),
- page loading (Loading),
- content optimization (Content),
- layout (UX / UI),
- conversion (Conversion Experience),
- data analysis (Data Experience).
SERP Experience, as building experiences at the level of the search results page, is a space that is still heavily underestimated by many SEO specialists. By its very nature, SEO touches the space related to the technical issues as well as content optimization of the website. However, looking from the perspective of the user experience, the optimization of the website in terms of the appearance of the website in search results, not the mere building of the visibility in search results, should be by default the first step that every website takes in the online world.
Regardless of whether you are a little-known e-commerce, a local business, a global brand or a creator of niche solutions for business, the first step to be taken before you sell anything is to allow customers to find you.
The Nielsen Norman Group drew attention to the First E-Commerce Law in 2012:
If the customer cannot find the product, he cannot buy it either
FAQ
What are the different types of search queries?
Depending on the search term entered, the appearance of the SERP results can vary significantly. There are currently 4 categories of query intent: Informational, Navigational, Commercial and Transactional.






